Stock image Membrane Receptor
Nerve Impulse: Central Nervous System Neural Network With Zoom On Ranvier's Node.
Image, 1.89MB, 5079 × 3514 jpg
Serotoninergic Synapse Where Nerve Impulses Are Transmitted Through Serotonin.
Image, 1.06MB, 3020 × 4455 jpg

Serotoninergic Synapse Where Nerve Impulses Are Transmitted Through Serotonin.
Image, 1.04MB, 3020 × 4455 jpg
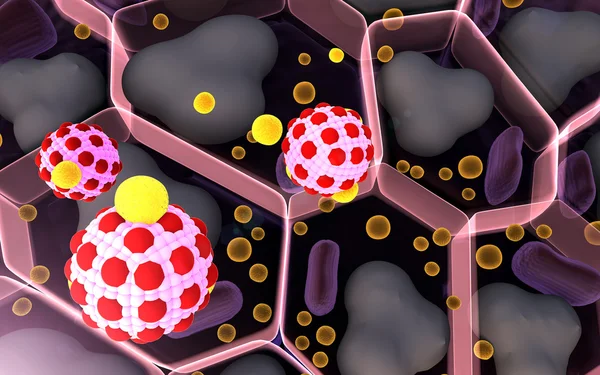
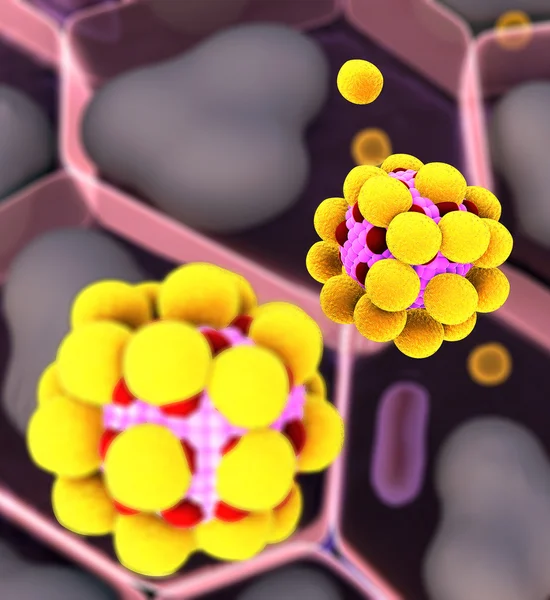
3d Computer Illustration Of Interleukin 13 And Its Receptor.IL-13 Is A Cytokine That Plays A Central Regulator Role In IgE Synthesis, Goblet Cell Hyperplasia, Mucus Hypersecretion, Airway Hyperresponsiveness, Fibrosis, It Is A Mediator Of Allergic I
Image, 5.59MB, 8000 × 6000 jpg
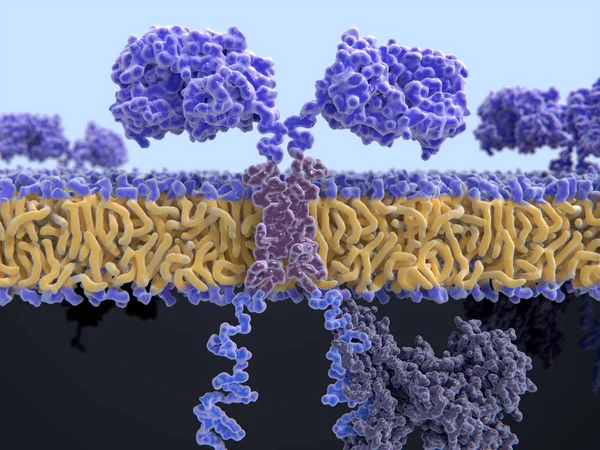
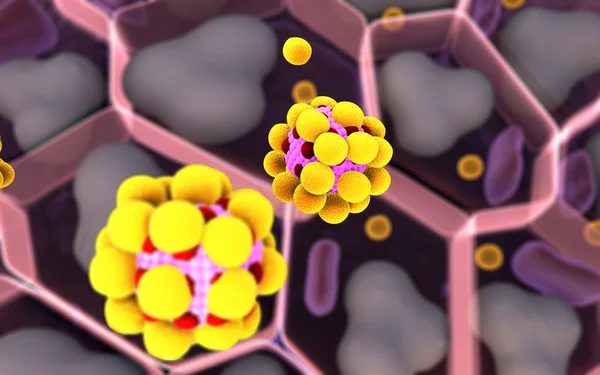
3d Computer Illustration Of A Chimeric Antigen Receptor. CARs Are Engineered Cell Receptors That Allow T Cells To Recognize And Attack Cancer Cells In A Specific Way. They Are Built By Connecting Several Functional Parts From Different Proteins.
Image, 8.45MB, 8000 × 6000 jpg

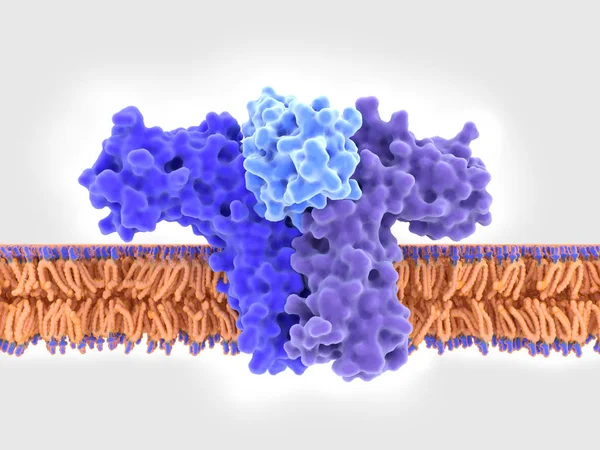
The Calcitonin Gene Related Peptide (yellow) Binds To Its Receptor (blue) On Neurons And Smooth Muscle Cells Of Cerebral Blood Vessels, Activating A Signal Cascade Through G-proteins (dark Blue) In This Cells That Leads To A Dilatation Of The Blood
Image, 7.55MB, 8000 × 6000 jpg
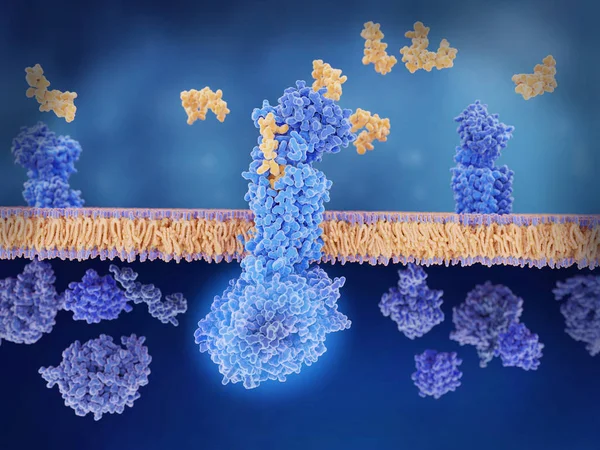
The Calcitonin Gene Related Peptide (yellow) Binds To Its Receptor (blue) On Neurons And Smooth Muscle Cells Of Cerebral Blood Vessels, Activating A Signal Cascade Through G-proteins (dark Blue) In This Cells That Leads To A Dilatation Of The Blood
Image, 6.01MB, 8000 × 6000 jpg

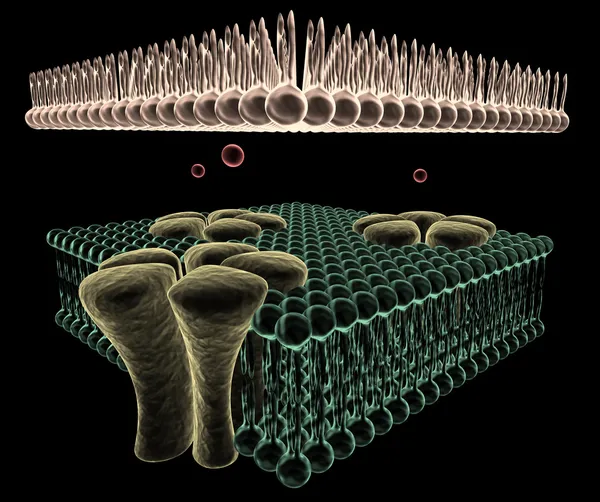
Ligand-dependent Ion Channel: Attachment Of A Particular Molecule Causes The Channel To Open.
Image, 1.14MB, 3020 × 4229 jpg

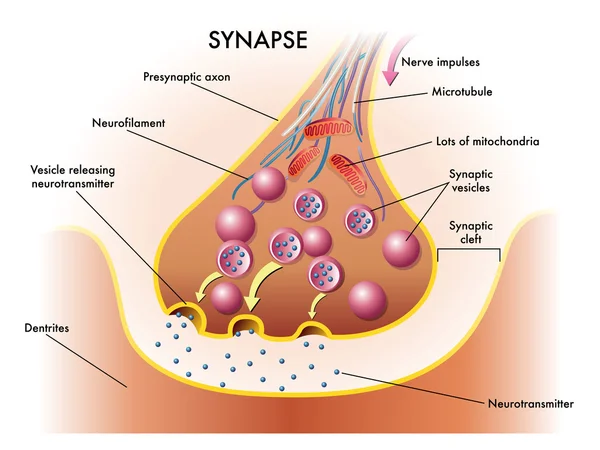
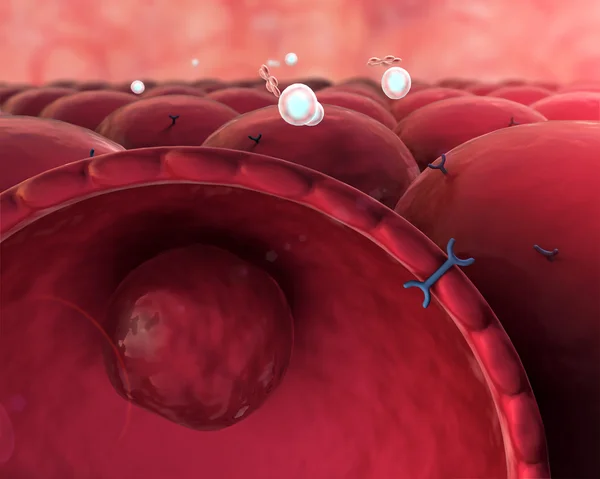
On A Cholinergic Synapse, The Nerve Impulse Is Transmitted Between The Two Neurons Thanks To Acetylcholine.
Image, 2.31MB, 4961 × 7016 jpg
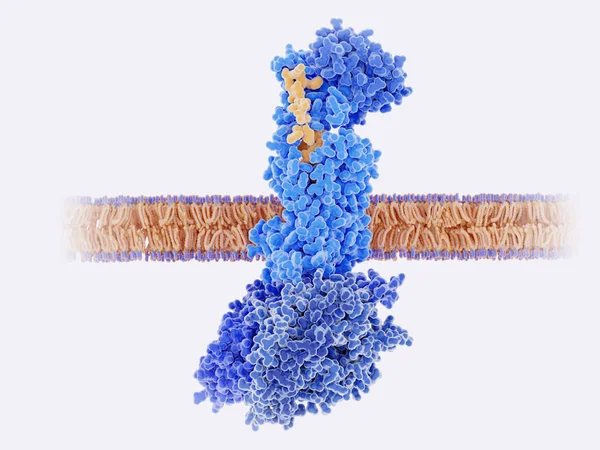
The Calcitonin Gene Related Peptide (yellow) Binds To Its Receptor (blue) On Neurons And Smooth Muscle Cells Of Cerebral Blood Vessels, Activating A Signal Cascade Through G-proteins (dark Blue) In This Cells That Leads To A Dilatation Of The Blood
Image, 4.43MB, 8000 × 6000 jpg
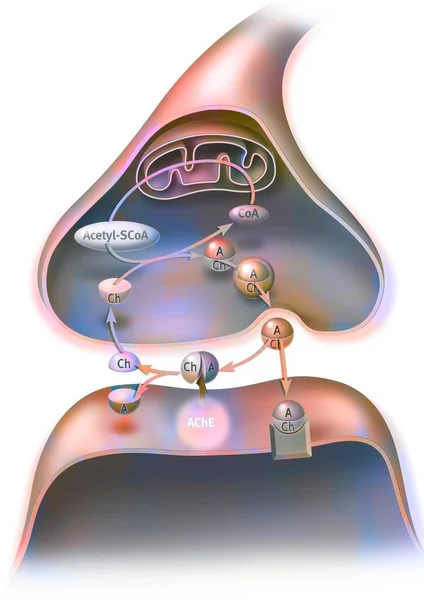
On A Cholinergic Synapse, The Nerve Impulse Is Transmitted Between The Two Neurons Thanks To Acetylcholine.
Image, 2.34MB, 4961 × 7016 jpg
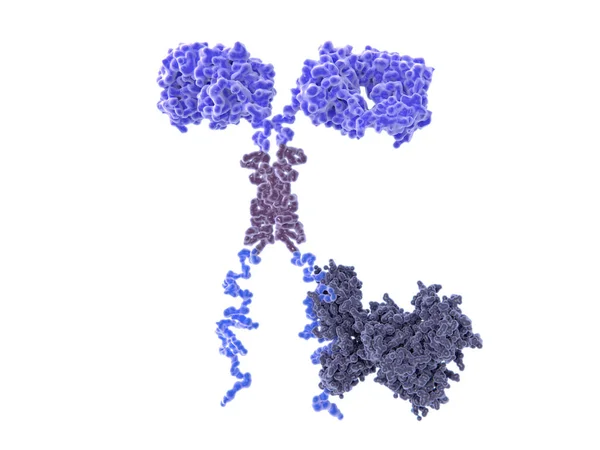
3d Computer Illustration Of A Chimeric Antigen Receptor. CARs Are Engineered Cell Receptors That Allow T Cells To Recognize/attack Specifically Cancer Cells. A Signal Protein Is Attached To The Intracellular Domain.
Image, 3.45MB, 8000 × 6000 jpg
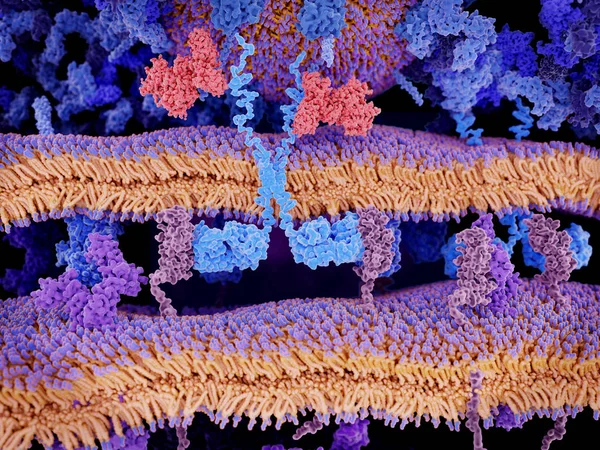
Engineered Receptors (light Blue) On The Surface Of A T-lymphocyte Bind Specifically To CD19-antigen Molecules (magenta) On A Leukemia Cell. This Activates A Signal Cascade In The T-cell Leading To The Segregation Of Vesicles That Contain Perforin An
Image, 11.44MB, 8000 × 6000 jpg
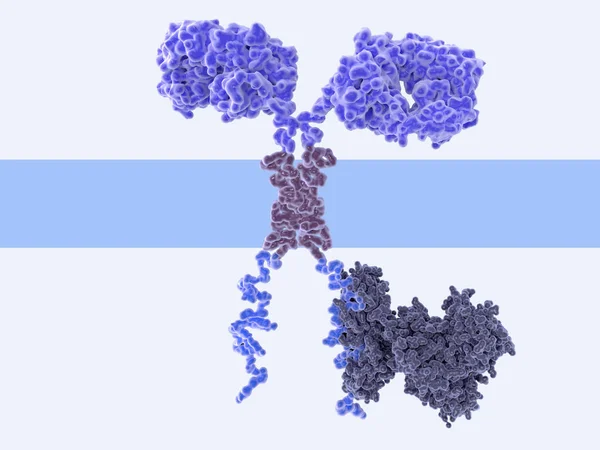
3d Computer Illustration Of A Chimeric Antigen Receptor. CARs Are Engineered Cell Receptors That Allow T Cells To Recognize/attack Specifically Cancer Cells. A Signal Protein Is Attached To The Intracellular Domain.
Image, 2.19MB, 8000 × 6000 jpg
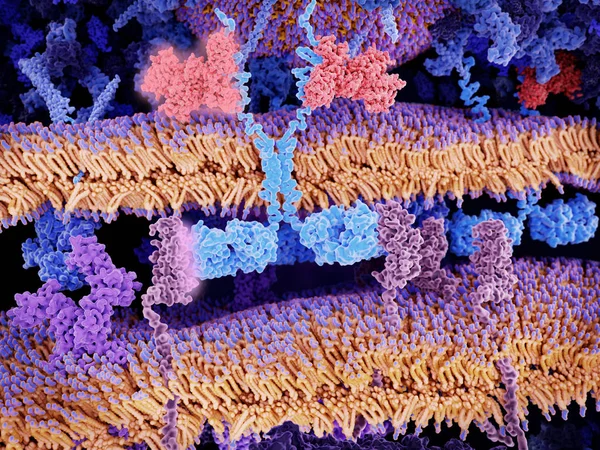
Engineered Receptors (light Blue) On The Surface Of A T-lymphocyte Bind Specifically To CD19-antigen Molecules (magenta) On A Leukemia Cell. This Activates A Signal Cascade In The T-cell Leading To The Apoptosis Of The Cancer Cell.
Image, 11.66MB, 8000 × 6000 jpg

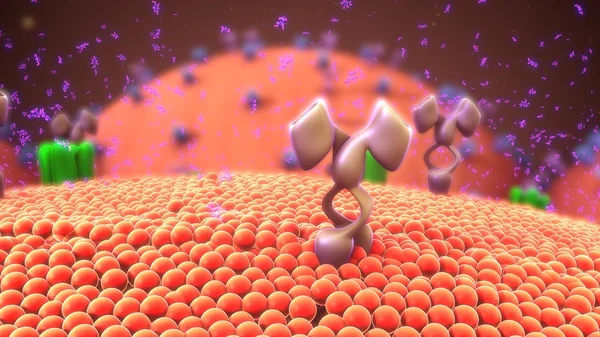
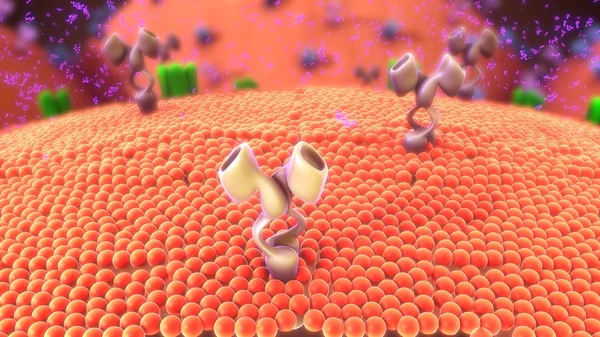
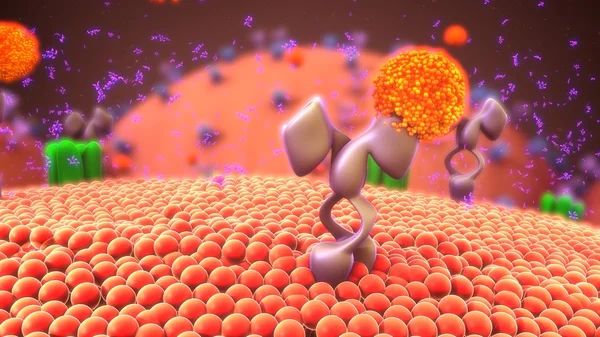
T-cell Receptors Are Similar To One Arm Of An Antibody. Like Antibodies, They Are Composed Of Two Chains. The Binding Site Is At The Tip Of The Molecule,
Image, 2.5MB, 8000 × 6000 jpg

Ligand-dependent Ion Channel: Attachment Of A Particular Molecule Causes The Channel To Open.
Image, 1.12MB, 3020 × 4229 jpg
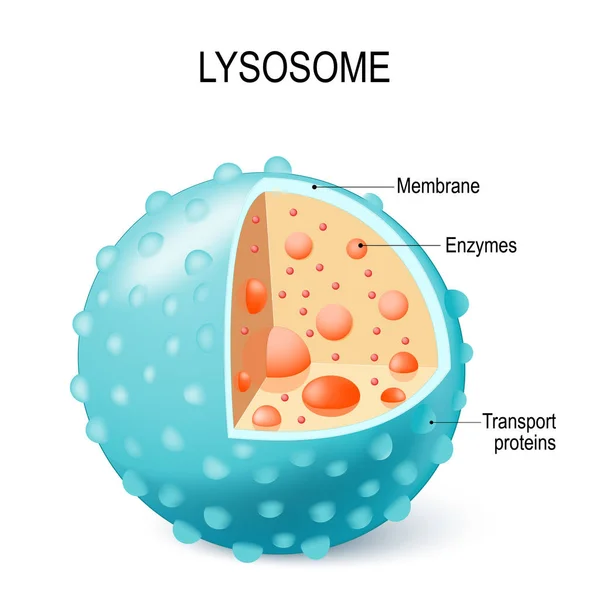
Anatomy Of The Lysosome: Hydrolytic Enzymes, Membrane And Transport Proteins. This Organelle Use The Enzymes To Break Down And Digest Food Particles, Engulfed Viruses Or Bacteria In The Cell. Vector Diagram For Medical Use
Vector, 6.8MB, 4230 × 4230 eps
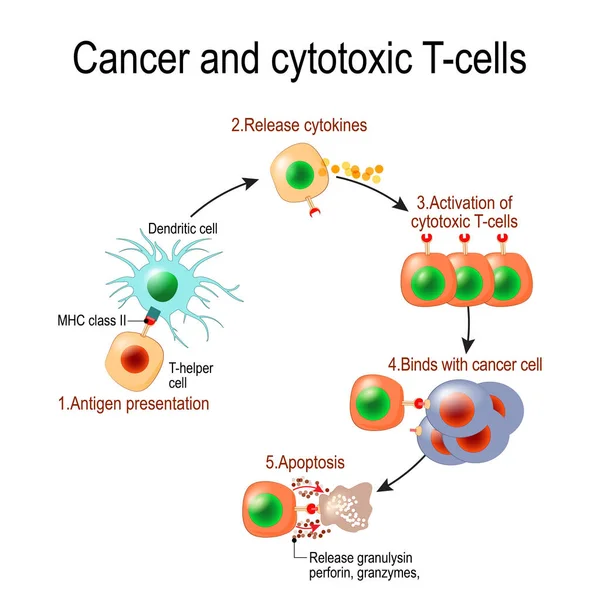
Cancer And Cytotoxic T-cells. T Lymphocyte Kills Cancer Cells. T-cell (immune Responses), Release The Perforin And Granzymes, And Attack Cancerous Cells. Through The Action Of Perforin, Granzymes Enter The Cytoplasm Of The Target Cell, And Lead To Ap
Vector, 1.01MB, 4050 × 4049 eps
Page 1 >> Next