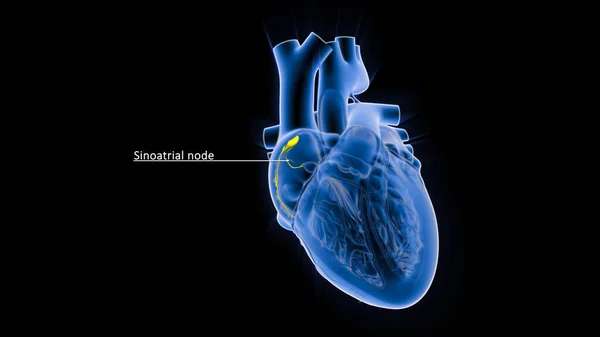
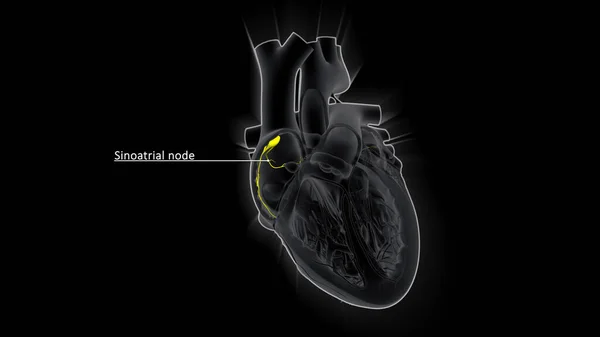
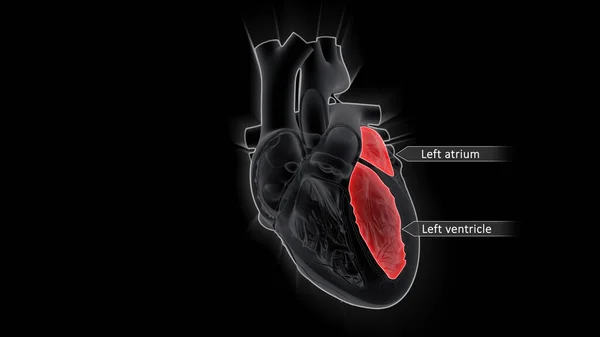
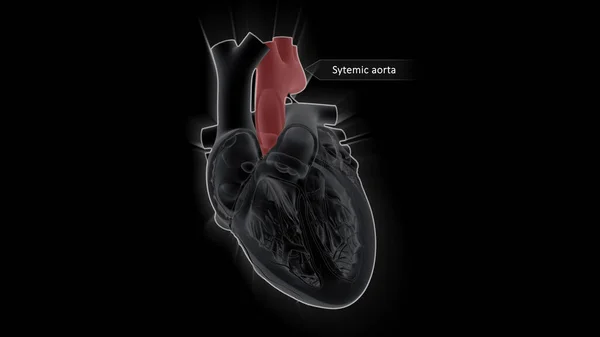
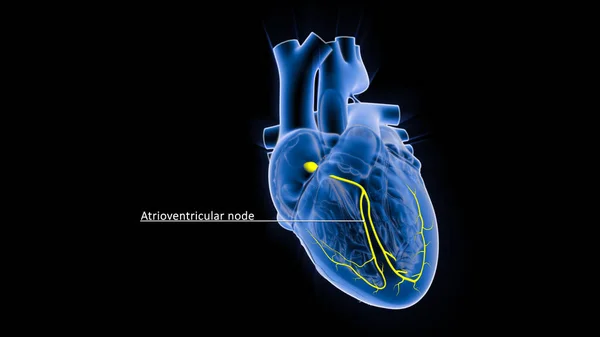
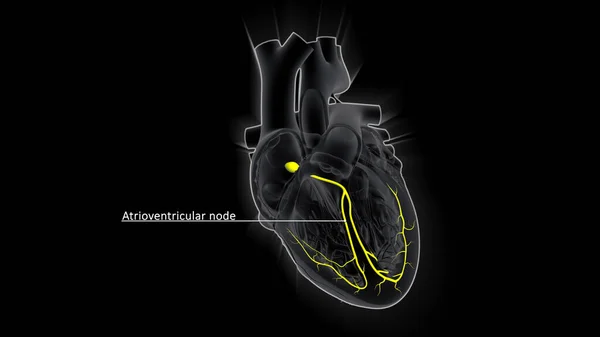
Stock image The AV node, which controls the heart rate, is one of the major elements in the cardiac conduction system. The AV node serves as an electrical relay station, slowing the electrical current sent by the sinoatrial (SA) node.
Published: Sep.24, 2021 09:16:25
Author: sciencepics
Views: 17
Downloads: 1
File type: image / jpg
File size: 1.15 MB
Orginal size: 3840 x 2160 px
Available sizes:
Level: silver