Stock image Transduction
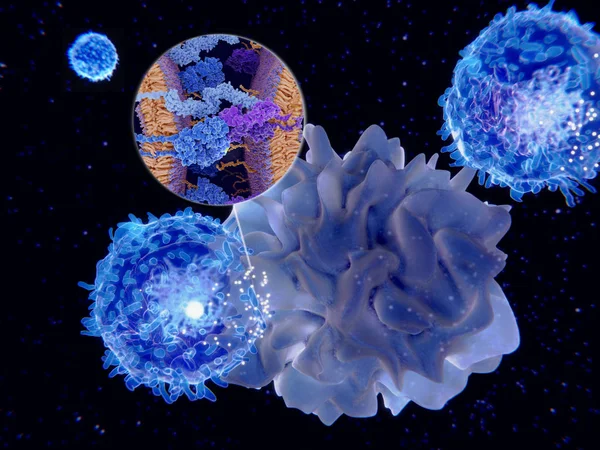
Dendritic Cells Present Antigens (green) To Lymphocytes Through Their Membran Bound MHC-molecules (violet). CD4 Molecules (light Blue) Bind To Other Portions Of The MHC, Strengthening The Interaction.
Image, 10.24MB, 8000 × 6000 jpg
Cancer Cells Express PD-L1 (orange) Proteins On Their Surface To Trick The Immune System. The Interaction Of PD-L1 With PD-1 Of T-cells Leads To A Down-regulation Of T-cells. The Antibody (yellow) Blocks This Interaction.
Image, 18.3MB, 8000 × 6000 jpg

Structure Of Human Hormone Insulin-like Peptide-3 Heterodimer, 3D Cartoon And Gaussian Surface Models, White Background
Image, 3.16MB, 10000 × 4000 jpg

Calmodulin, Inactive-calcium Free (left), And Activated (right) Conformations,
Image, 2.57MB, 8000 × 6000 jpg

The Sense Of Smell Detects Airborne Molecules Via Olfactory Receptors In The Nasal Cavity, Sending Signals To The Brain For Perception
Image, 1.95MB, 5670 × 3971 jpg

Cellular Health Concept, Processes That Contribute To The Optimal Functioning Of Organism Cells, Mind Map Sketch
Image, 14.22MB, 5600 × 3733 jpg
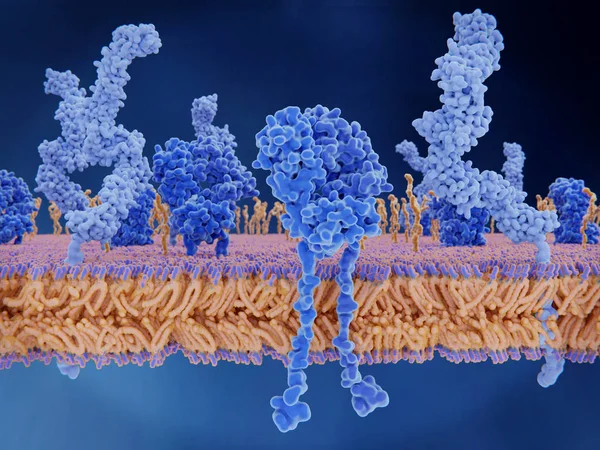
The T-cell Receptor Activates The Immune Response To Antigens In T-lymphocytes. T-cell Receptors (dark Blue), CD4 Molecules (light Blue), Glycolipids (orange). 3d Rendering. Illustration
Image, 3.11MB, 8000 × 6000 jpg
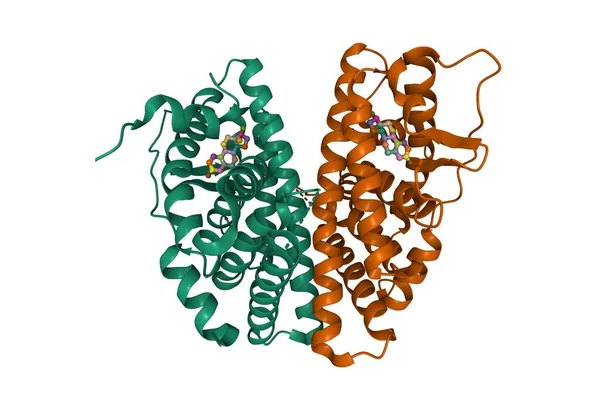
Estrogen Receptor Beta Dimer In Complex With Estradiol, 3D Cartoon Model, Chain Id Color Scheme, Based On PDB 5toa, White Background
Image, 2.91MB, 6000 × 4000 jpg
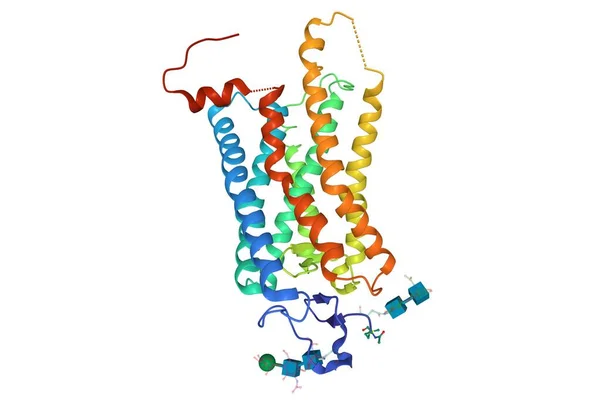
Crystal Structure Of A Photoactivated Rhodopsin, 3D Cartoon Model Isolated, White Background
Image, 1.92MB, 6000 × 4000 jpg

Structure Of Human Activin A Homodimer, 3D Cartoon Model, White Background
Image, 1.88MB, 6000 × 4000 jpg

Chemical Formula, Skeletal Formula And 3D Ball-and-stick Model Of Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate (cAMP), White Background
Image, 1.42MB, 6500 × 4500 jpg
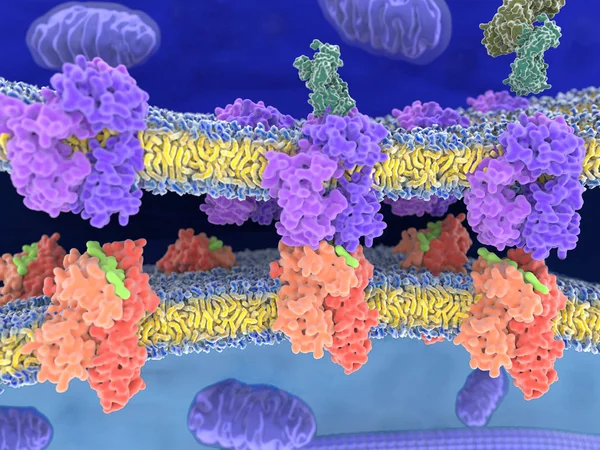
T-cell Receptor In Complex With The MHC Class II-peptide Complex. The Antigen (light Green) Is A Peptide From A Tumor Cell, Bacteria Or Virus. Different Stages Of The Interaction. 3D-Rendering. Illustration
Image, 9.21MB, 8000 × 6000 jpg

Calmodulin, A Crucial Messenger Protein. Calmodulin Has 4 Ca2+ Binding Sites.
Image, 2.97MB, 8000 × 6000 jpg
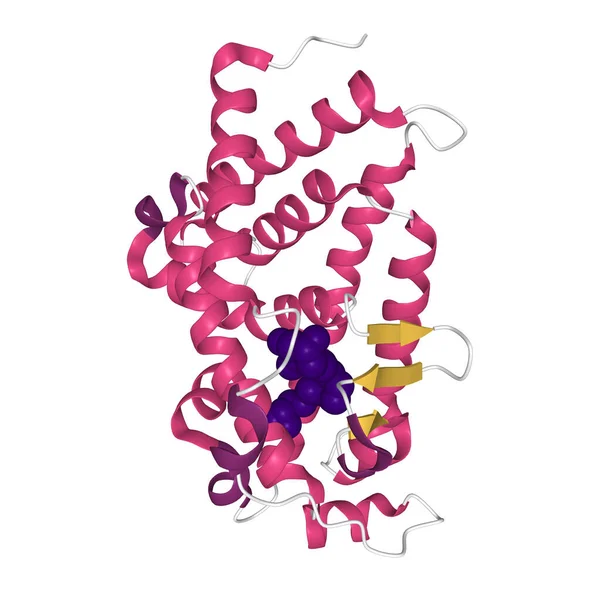
Crystal Structure Of VDR Ligand Binding Domain Complexed To Calcipotriol (blue), 3D Ball-and-stick Model, White Background
Image, 2.54MB, 4096 × 4096 jpg
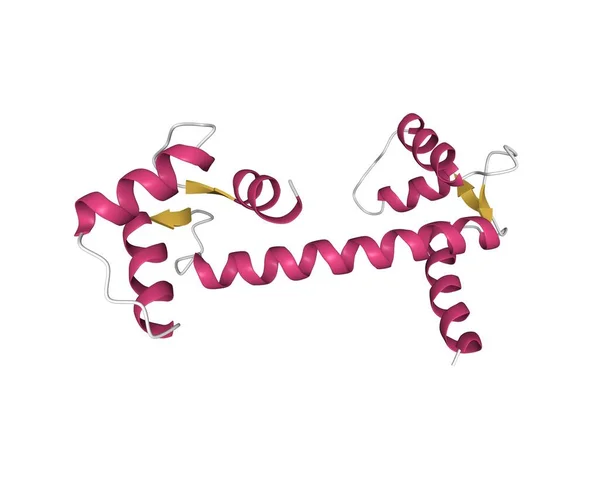
Structure Of Human Calmodulin, 3D Cartoon Model With The Differently Colored Elements Of The Secondary Structure, White Background
Image, 1.2MB, 5000 × 4000 jpg
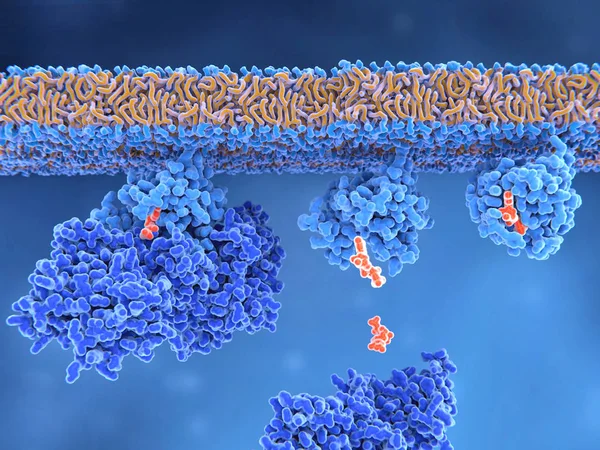
3d Computer Illustration Of The Activation Process Of A Ras Protein. Inactive Ras Protein (left) Is Activated By A GEF Protein Opening The Binding Site And Allowing GDP To Exit. Afterwards GTP Can Bind To RAS Turning It Into The Active Form (right).
Image, 7.61MB, 8000 × 6000 jpg

Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphat (cAMP, Red) Is A Second Messenger Used For Signal Transduction Through The Activation Of Various Protein Kinases (blue). The One In The Foreground Is Protein Kinase A. Source: PDB Entry 3tnp.
Image, 7MB, 8000 × 6000 jpg

Guanosine Triphosphate (GTP) Molecule, It Is Used In Synthesis Of RNA And As A Source Of Energy For Protein Synthesis. Structural Chemical Formula And Molecule Model. Vector Illustration
Vector, 0.51MB, 5000 × 3409 eps
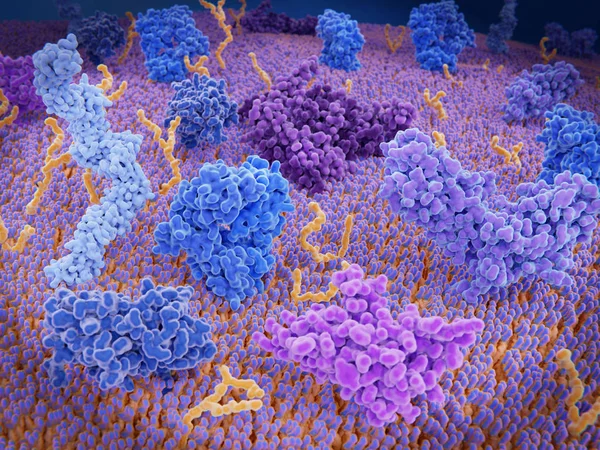
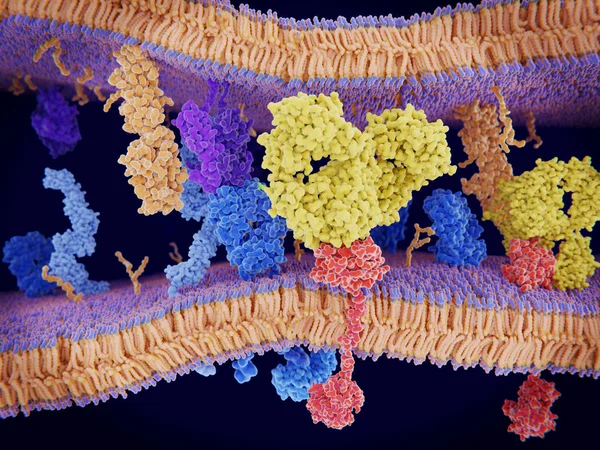
Immunologically Active Proteins On A T-cell. TCR (blue), CD-4 (light Blue), CD-28 (dark Blue), PD-1 (magenta), CTLA-4 (violet), Ca-channel (dark Violet). The T-cell Receptor, CD-4 And CD-28 Activate T-cells, While PD-1 And CTLA-4 Inhibit The Activat
Image, 10.2MB, 8000 × 6000 jpg
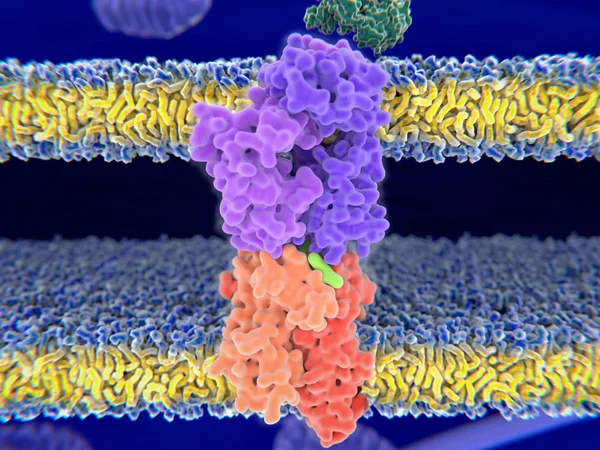
T-cell Receptor In Complex With The MHC Class II-peptide Complex. The Antigen (light Green) Is A Peptide From A Tumor Cell, Bacteria Or Virus. Complex Embedded In The Membranes. 3D-Rendering. Illustration
Image, 7.59MB, 8000 × 6000 jpg
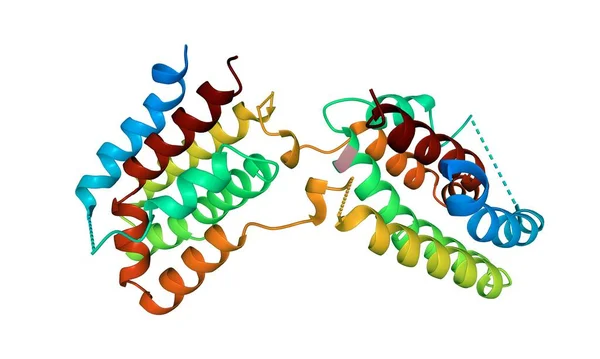
Structure Of Human Interleukin-10, 3D Cartoon Model Isolated, White Background
Image, 2.14MB, 5000 × 3000 jpg

3D Image Of Inositol Skeletal Formula - Molecular Chemical Structure Of Carbocyclic Sugar Vitamin B8 Isolated On White Background
Image, 6MB, 8226 × 6888 jpg
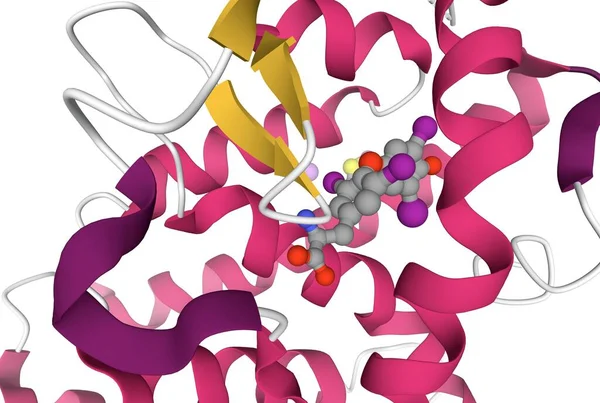
Thyroxine-thyroid Hormone Receptor Interactions, 3D Cartoon Model, White Background
Image, 3.43MB, 6077 × 4083 jpg

CAMP Cyclic Adenosine MonoPhosphate - Second Messenger Important In Many Biological Processes, Acronym Text On Blackboard
Image, 11.5MB, 5760 × 3840 jpg
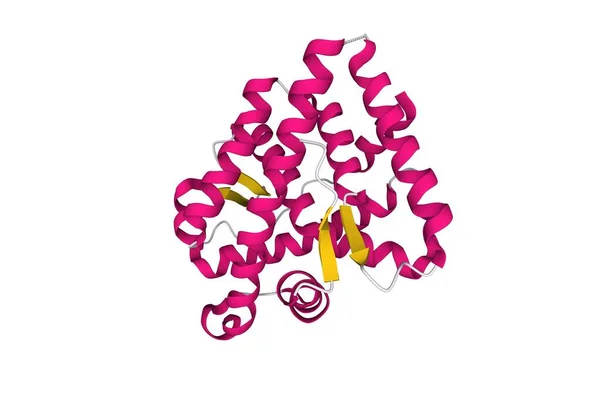
Structure Of The Human Androgen Receptor, 3D Cartoon Model With The Differently Colored Elements Of The Secondary Structure, White Background
Image, 1.8MB, 6000 × 4000 jpg
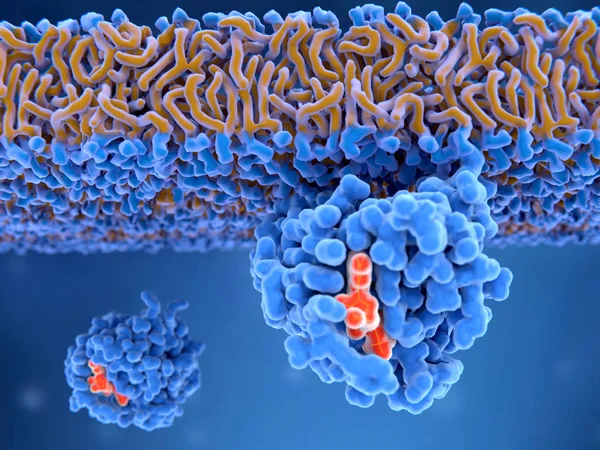
3d Computer Illustration Of An Activated Ras Protein. Ras Proteins Are Involved In Transmitting Signals Within Cells Turning On Genes Involved In Cell Growth, Differentiation And Survival. Mutations In Ras Genes Can Lead To Permanently Activated Prot
Image, 4.61MB, 8000 × 6000 jpg

T-cell Receptor In Complex With The MHC Class II-peptide Complex. The Antigen (light Green) Is A Peptide From A Tumor Cell, Bacteria Or Virus. Different Stages Of The Interaction. 3D-Rendering. Illustration
Image, 7.31MB, 8000 × 6000 jpg
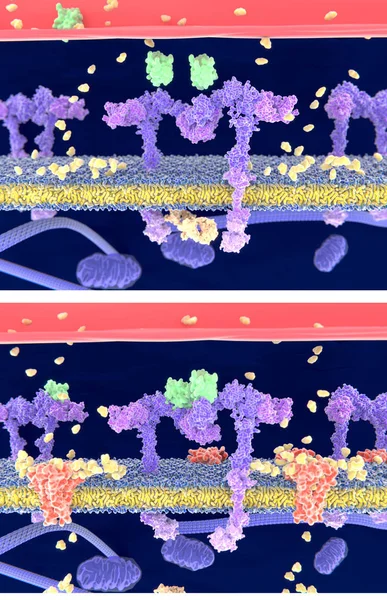
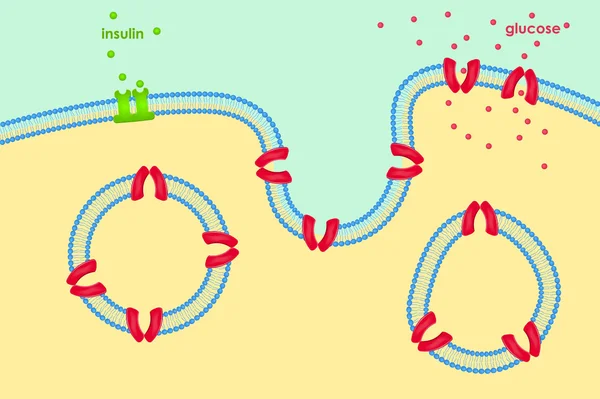
Insulin (green) Binding To The Insulin Receptor (violet) Activates The Transport Of Glucose (yellow) Into The Cell (depicted In 2 Phases) - Illustration
Image, 4.57MB, 4000 × 6200 jpg
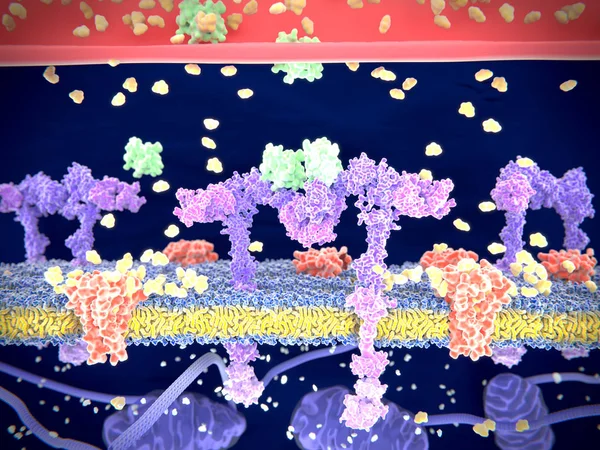
Insulin (green) Binding To The Insulin Receptor (violet) Activates The Transport Of Glucose (yellow) Into The Cell. Illustration
Image, 6.21MB, 8000 × 6000 jpg
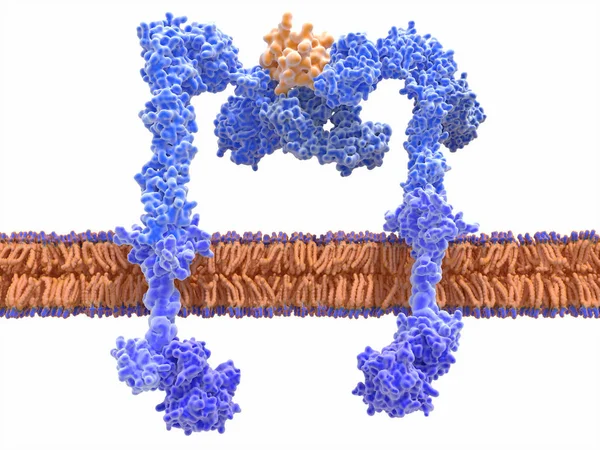
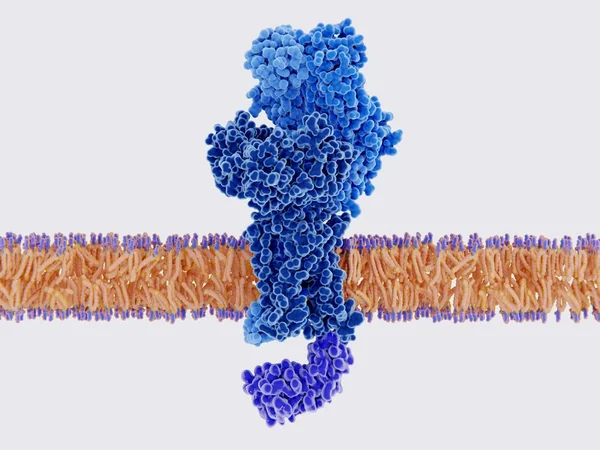
The Insulin Receptor (blue) Is A Transmembrane Protein, That Is Activated By Insulin (orange). Insulin Binding Induces Structural Changes Within The Receptor That Finally Leads To The Activation Of The Glucose Transporter Protein.
Image, 12.2MB, 8000 × 6000 jpg
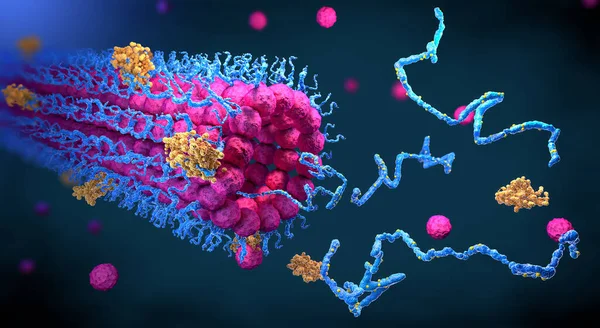
Protein Enzymes Fold Into Their Structure To Fulfill Their Function - 3d Illustration
Image, 13.4MB, 7300 × 4000 jpg
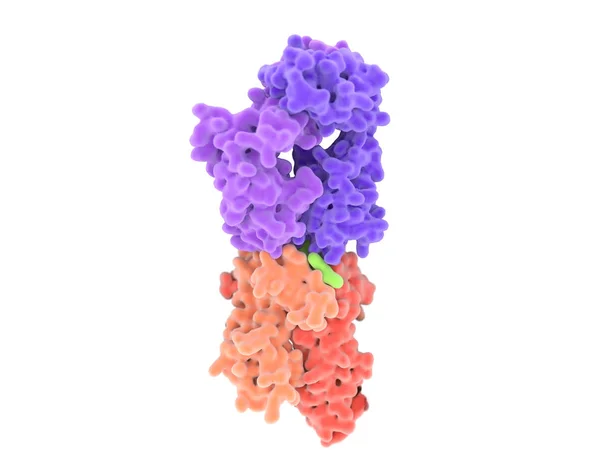
T-cell Receptor In Complex With The MHC Class II-peptide Complex. The Antigen (light Green) Is A Peptide From A Tumor Cell, Bacteria Or Virus. Different Stages Of The Interaction. 3D-Rendering. Illustration
Image, 2.17MB, 8000 × 6000 jpg
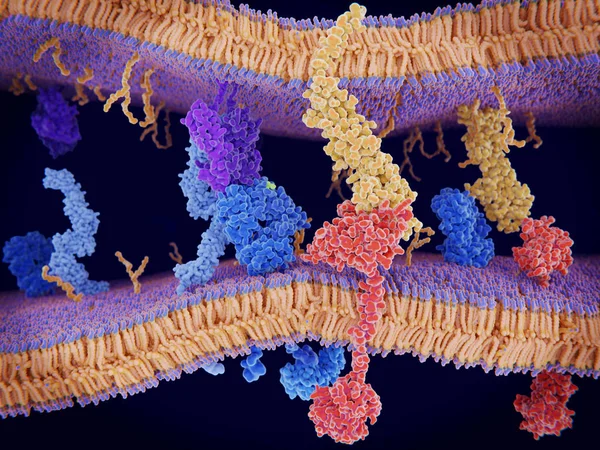
PD-1 (red) Extends From The Surface Of A T-cell And Interacts With The Ligand Protein PD-L1 (yellow) From A Antigen Presenting Cell. Although The T-cell Has Been Activated Through The Interaction Of A T-cell Receptor (blue) And A MHC Protein (viole
Image, 18.32MB, 8000 × 6000 jpg

Hormones, Receptors And Target Cells. Each Type Of Hormone Is Designed Only Certain Cells. These Cells Will Have Receptors On Them That Are Specific For A Certain Hormone. Vector Illustration For Medical, Biological, And Educational Use
Vector, 2.77MB, 5013 × 5012 eps
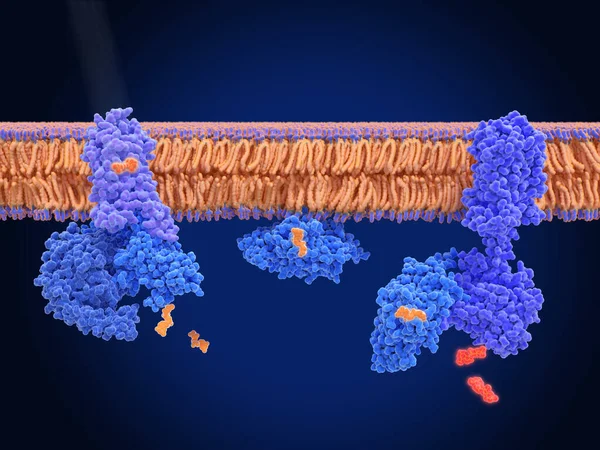
Rhodopsin Is A Light Sensitive G-protein Coupled Receptor With Retinal As Cofactor. That Stimulates The G-protein Transducin, Resulting In The Liberation Of Its Subunit. This GTP-bound Subunit In Turn Activates CGMP Phosphodiesterase.
Image, 8.93MB, 8000 × 6000 jpg

Structure Of Human Interleukin-11, 3D Cartoon Model Isolated, White Background
Image, 2.35MB, 6000 × 4000 jpg
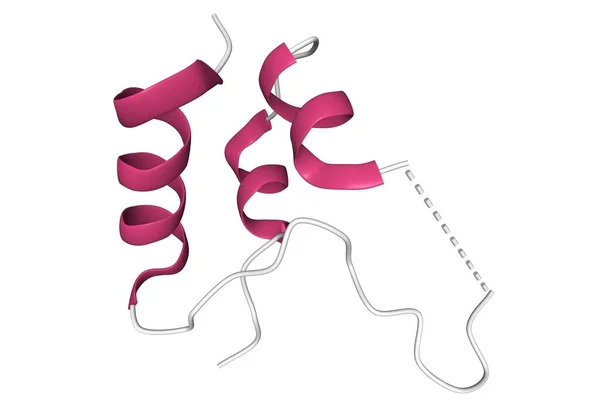
Structure Of Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 (IGF-1), 3D Cartoon Model Of The Tertiary Structure With The Elements Of The Secondary Structure Colored, White Background
Image, 1.25MB, 6000 × 4000 jpg
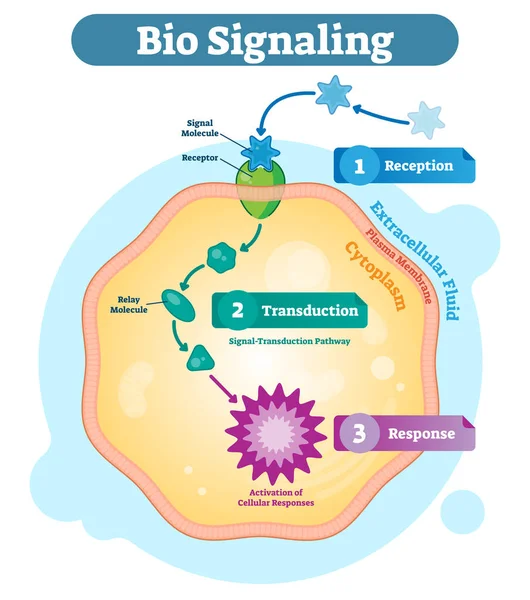
Bio Signaling Cell Communication Network System, Micro Biological Anatomy Labeled Diagram Vector Illustration With Receptor, Transduction And Response Activity.
Vector, 5.4MB, 4167 × 4709 eps
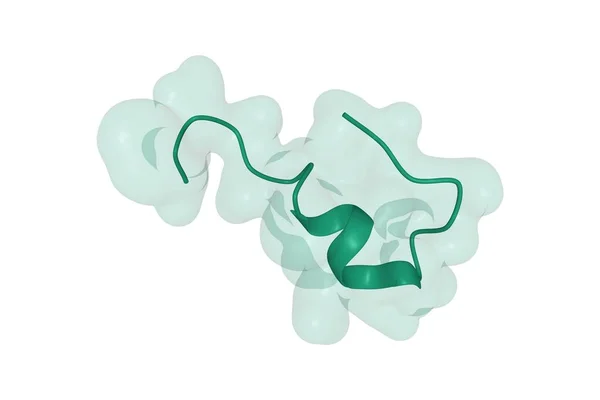

Structure Of Human Endothelin-1, A Polypeptide Hormone Regulator Of Blood Pressure, 3D Combined Surface-cartoon Model Isolated, White Background
Image, 1.2MB, 6000 × 4000 jpg
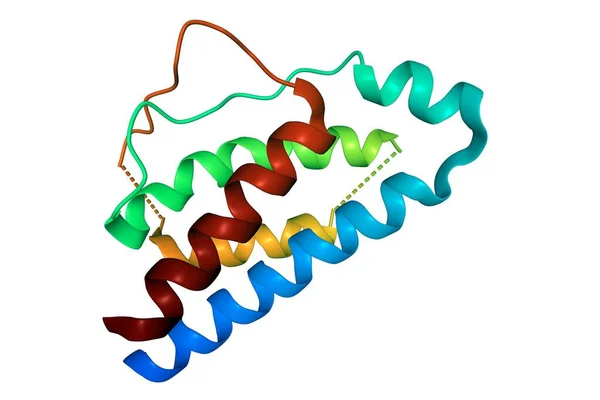
Structure Of Human Interleukin-2, 3D Cartoon Model Isolated, White Background
Image, 2.46MB, 6000 × 4000 jpg
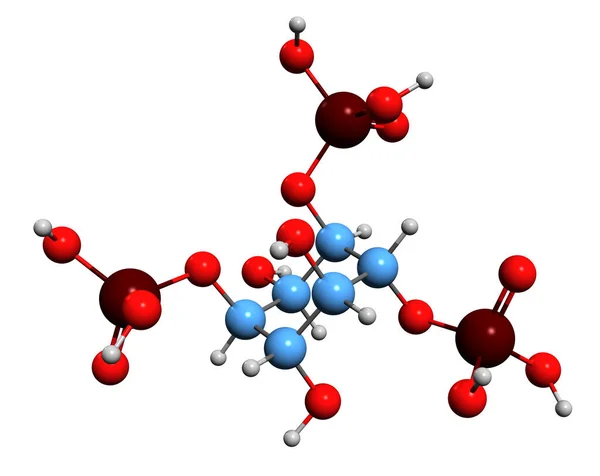
3D Image Of Inositol Trisphosphate Skeletal Formula - Molecular Chemical Structure Of Inositol Phosphate Signaling Molecule Isolated On White Background
Image, 3.87MB, 6943 × 5520 jpg
Page 1 >> Next