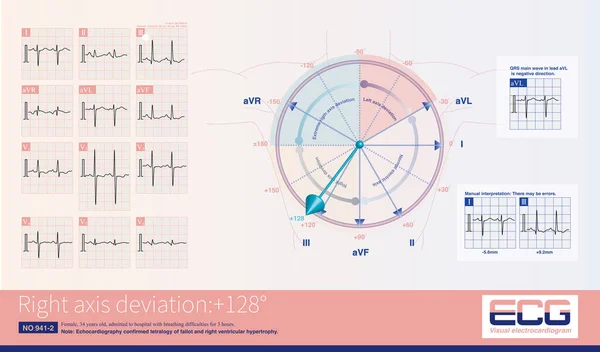
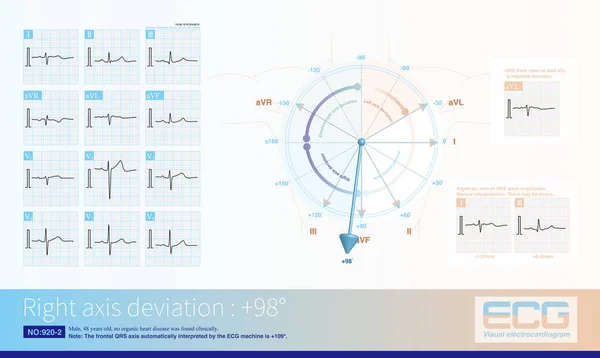
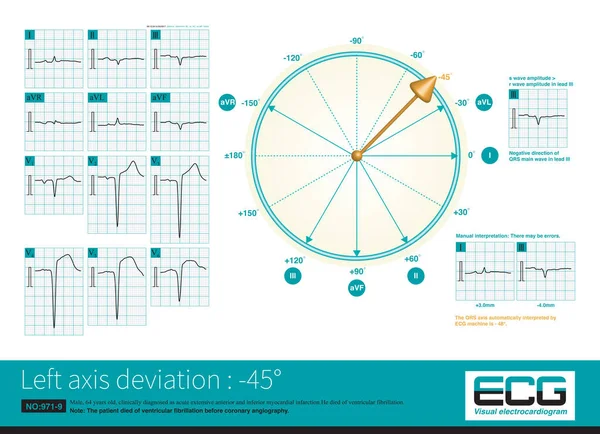
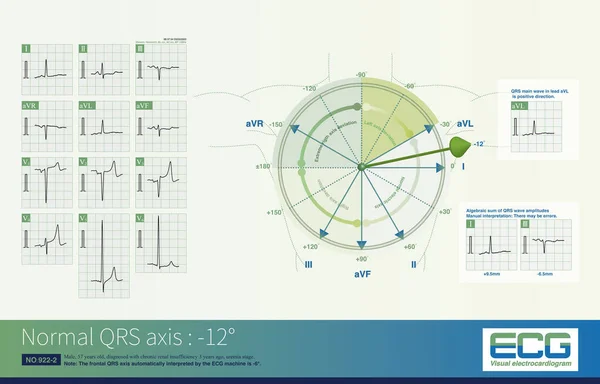
Stock image In acute left main occlusion, the left ventricular myocardium is massively ischemic and necrotic, the excitatory potential of the left ventricle is weakened, and the axis may deviate to the right .

Published: May.15, 2024 15:35:53
Author: asia11m
Views: 2
Downloads: 0
File type: image / jpg
File size: 12.47 MB
Orginal size: 10000 x 6364 px
Available sizes:
Level: beginner